World Geography
ASIA
Asia – World
Geography
Asia is the world largest
continent, having
an area of 44,444,100 sq
km.
It covers 8.8% of the Earth’s total surface area with a population
of 4.4 billion which is 60
% of the world’s total population.
It is a continent of contrast in relief,
temperature, vegetation and people also.
Asia is to the east of
the Suez Canal, the Ural River, and the Ural Mountains, and south of the
Caucasus Mountains and the Caspian and Black Seas.
It is bounded on the east
by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean and
on the north by the Arctic Ocean.
The earth’s highest and lowest places are both in Asia:
- The highest place on earth: Mount
Everest
- The lowest place on earth: Dead
Seashore
Only some of the Indonesian group of
Islands is located to the south of equator in the Southern Hemisphere.
North-South
Extent : 6,440 km East-West Extent : 9,650 km
Interesting
Geographical facts about Asia
|
|
Asia
is the largest continent and occupies about 30% of the total area of the Earth.
It has extremely diverse geographic features as well as climates. Climates range from arctic and
subarctic in Siberia to tropical in southern India and Southeast Asia.
Interesting geographical fact
about Asia
1. It is located primarily in the Eastern
and Northern Hemispheres.
2. The Equator, Tropic of Cancer and Arctic
Circle passes through it.
3. It is surrounded by the Indian
Ocean in the south; Arctic Ocean in the north; the Pacific Ocean
in the east; Ural Mountains, Caspian Sea, Black Sea and the Mediterranean
Sea in the west.
4. It is separated from
Africa by the Red Sea and Suez Canal.
5. It
is separated from North America by Bering Strait.
6. Important Peninsulas: Arabian
Peninsula, Indo-Chinese Peninsula and Deccan Peninsula.
7. Arabian Peninsula is the
largest Peninsula in the World.
8. Important Island groups: Andaman
and Nicobar, Indonesia, Philippines and Japan.
9. The deepest trench of the
world: Mariana Trench lies in the Pacific Ocean near
Philippines.
10. Pamir Plateau is
known as ‘Roof of the World’ situated in the Central Asia.
Regional
Divisions of Asia
Asia can be divided into six physiographic
divisions:
1.
Central Asia: Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan,
Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan
2.
Eastern Asia: China, Hong Kong, Japan, North
Korea, South Korea, Macau, Mongolia, Taiwan
3.
Northern Asia: Russia
4.
South-eastern Asia: Brunei, Myanmar, Cambodia,
Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Timor-Leste,
Vietnam.
5.
Southern Asia: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India,
Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, Sri Lanka.
6.
Western Asia: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Cyprus,
Georgia, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, State of Palestine,
Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, Yemen.
|
|
Major
Physical Divisions of Asia
- The Northern Lowlands
- The Central Mountains
- The Central and Southern Plateaus
- The Peninsulas
- Deserts
- The Great River Plains
- Island Groups
1. The Northern Lowlands
The Northern Lowlands are
the extensive plain areas that comprise of several patches of
lowlands of this large continent.
The major lowlands are:
A.
Great Siberian plain
·
It
extends between the Ural Mountains in the west and the river Lena in the
east. It is the largest lowland in the world covering an area of
1,200,000 square miles approx.
B.
Manchurian Plain
- It is the area adjoining Amur river and its
tributaries of the northern part of China with an area of 135,000
square miles approx.
C.
Great Plains of China
- It is contributed by two major rivers of
China, Hwang Ho and Yangtze river which covers an area of 158,000
square miles approx.
D. Tigris-Euphrates plains
E.
Ganga plains
F.
Irrawaddy plains
2. The Central Mountains
Ø These are the prominent and
extensive mountain ranges that cover the parts of Central Asia.
Ø They consist of Pamir and
Tian Shan ranges and extending across portions of Afghanistan, China,
Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan.
|
Continued------ Major Physical Divisions of Asia 1.
The
Northern
Lowlands 2.
The Central Mountains 3.
The Central and Southern Plateaus 4.
The Peninsulas 5.
Deserts 6.
The Great River Plains 7.
Island Groups |
Ø These mountain ranges are
designated as biodiversity hot spots by Conservation International which covers
several mountains and alpine eco-regions of Central Asia.
Ø It encompasses several habitat
types, including mountain grasslands and shrub lands, temperate coniferous
forests, and alpine tundra.
Ø A mountain knot is a
junction of two or more mountain ranges. The two main mountain knots in
Asia are:
1. The Pamir Knot is the
junction of five mountain ranges they are the Sulaiman, the Hindu
Kush, the Kunlun, the Karakoram, and the Himalayan ranges. Mount Everest, the
highest peak in the world in the Himalayan range.
2. The Armenian Knot is
connected to the Pamir Knot by the Elburz and the Zagros Ranges that
originate in the Armenian Knot. The Tien Shan and the Altai are other mountain
ranges in Asia.
Peaks of Asia
Ø Mount Everest (8848 m),
Nepal-Tibet, China border
Ø K2 (8,61,1 m), Pakistan-China
Ø Kangchenjunga (8,586 m),
Nepal-Sikkim (India).
Ø Lhotse (8,516 m), Nepal-Tibet,
China
Ø Makalu (8,462 m), Nepal-Tibet,
China
Ø Cho Oyu (8,201 m), Nepal
|
Continued------ Major Physical Divisions of Asia 1.
The
Northern
Lowlands 2.
The Central Mountains 3.
The Central and Southern Plateaus 4.
The Peninsulas 5.
Deserts 6.
The Great River Plains 7.
Island Groups |
Ø
Mountains-Ranges
3. The Central and
Southern Plateaus
Plateaus are the land areas having a relatively
that surface considerably raised above adjoining land on at least one side, and
often cut by deep canyon.
Major Plateaus of Asian Continent –
|
Plateau |
Location |
Types |
|
Ladakh |
Between
Karakoram and Himalaya mountain ranges |
Intermontane |
|
Tibet |
Between
Kulun and Himalayan Mountain range |
Intermontane |
|
Yunan |
Situated
on the southeast of the Tibet Plateau and separated from Szechuan Basin
extensive fertile land by the range of Mountains |
Piedmont |
|
Pamir |
Well
connected to the range of mountains such as The Himalayas with the Tian Shan,
Karakoram, Kunlun, and the Hindu Kush ranges on all sides |
Intermontane |
|
Armenian |
Present
in between Caspian and the Black Sea |
Piedmont |
|
Iranian |
Present
in between Zagros Mountains, Caspian Sea, Turkmen-Khorasan Mountain Range |
Piedmont |
|
Mongolian |
Surrounded
by the Greater KHinggan Mountains in the east, the Yin Mountains to the
south, the Altai Mountains to the west, and the Sayan and Khentii mountains
to the north |
Intermontane |
|
Shan |
Stretched
in the Pegu Yoma and Arkan Yoma in the eastern part of Myanmar, |
Intermontane |
|
Deccan |
Extended
in between the Western Ghats in the west and the Eastern Ghats in the east of |
Intermontane |
|
Anatolian |
Enclosed
between Pontic mountain ranges in the South and Taurus in the southwest |
Volcanic |
|
Intermontane Plateaus
Ø The plateaus which are
bordering the mountain ranges (generally fold mountains) or are partly or
fully enclosed within them are the intermontane plateaus. Ø The word ‘intermontane’ means
‘between mountains’. Ø Intermontane plateaus are the
highest in the world. Ø They have nearly horizontal
rock layers which are raised to very heights by vertical movements of the
earth. Ø Examples: The Plateau of Tibet is an
example of the intermontane plateau which is surrounded by the fold mountains
like the Himalayas, the Karakoram, the Kunlun and the Tien Shan. Piedmont Plateaus
Ø Plateaus which is
situated at the foot of a mountain and is locked on the other side by a plain
or a sea/ ocean is called as a piedmont plateau. Ø The word
‘piedmont’ means ‘foot of a mountain’. Ø They are also
called as Plateaus of denudation as the areas once were high
to the level of mountains, have now been reduced to the foot level of the
mountain by various agents of erosion. Ø Examples: The Malwa
Plateau is an example of piedmont plateau. |
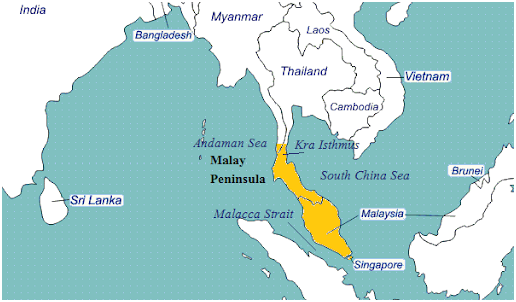
4. Peninsulas
A peninsula is a mass of land
surrounded by water but attached to the mainland. The Deccan plateau
region is also a peninsula. The major peninsulas of Arabia,
India, and Malay are in southern Asia. The Kamchatka peninsula lies
in northeastern Asia.
5. Deserts
Asia has some big deserts such as
the Gobi, the Takla Makan, the Thar, the Kara-Kum, and
the Rub-al-Khali Deserts.
The Rub’ al Khali desert, considered
the world’s largest sand sea, covers an area larger than France across
Saudi Arabia, Oman, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen.
6. (a) Islands of Asia
Asia also has a cluster
of islands, also called an archipelago. An archipelago sometimes called an
island group or island chain, which is formed close to each other in large
clusters. Indonesia, Philippines, Japan, Andaman,
and Nicobar are some examples of archipelagos.
6. (b) Drainage of Asia
The drainage of Asia consists of mighty oceans,
extensive seas, lengthy rivers, and their tributaries and distributaries, major
lakes, etc.
Oceans: Asian continent is
surrounded by three major ocean from three sides such as
A.
The Pacific Ocean – It covers the eastern part
of Asia where major rivers of eastern Asia drain, such as Menam Mekong, Xi
Jiang, Chang Xiang, Huang Ho, and Amur.
B.
The Indian Ocean – It covers the southern part
of Asia and the major rivers that flow into the Indian Ocean are Tigris,
Euprates, the Indus, the Ganga, Brahmaputra, Irrawaddy, Salween.
C.
The
Arctic Ocean – It covers the Noth east part of Asia and consists of three
major rivers such as Ob, Yenisey, and Lena.
Seas:
As the continent is covered by sea from its three
sides, It has also characterized by the long stretch of bay and gulf.
Major seas contributing to Asian
Drainage are Andaman Sea, Arabian Sea, Banda Sea, Barents Sea, Bering
Sea, Black Sea, Caspian Sea, East Siberian Sea, Java Sea, Kara Sea, Laccadive
Sea, Sea of Japan, Sea of Okhotsk. The South China Sea and the Yellow Sea.























No comments:
Post a Comment